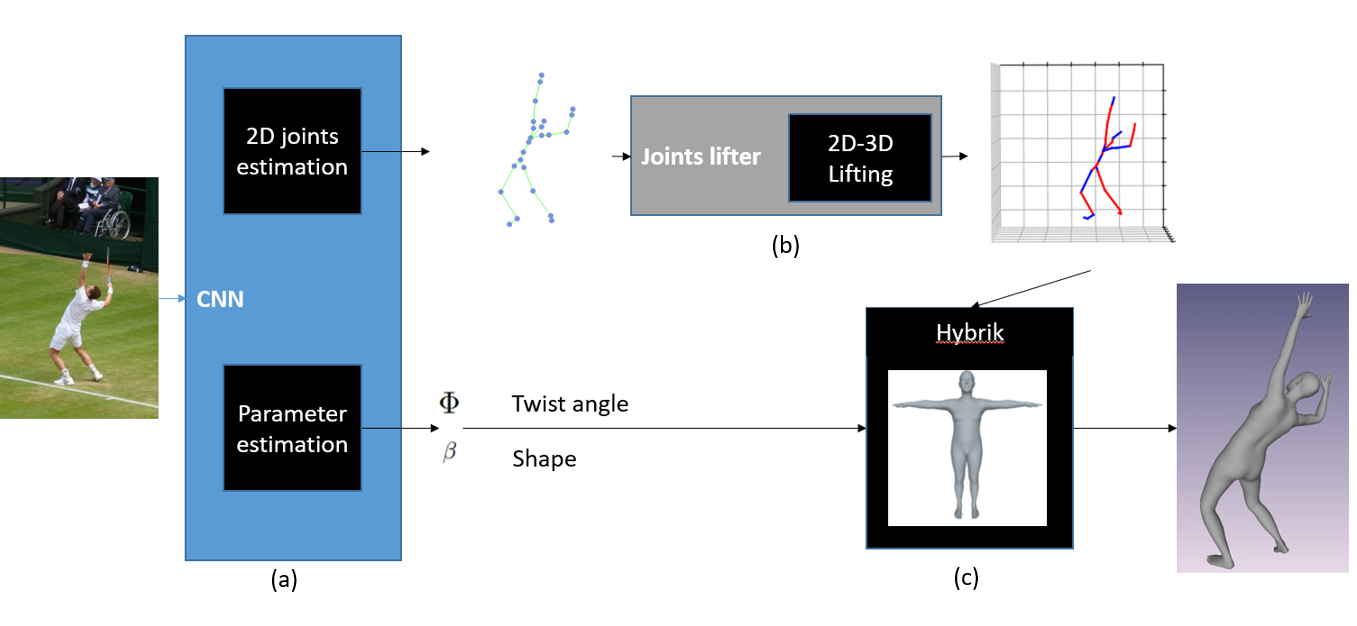
Flowchart for our system.
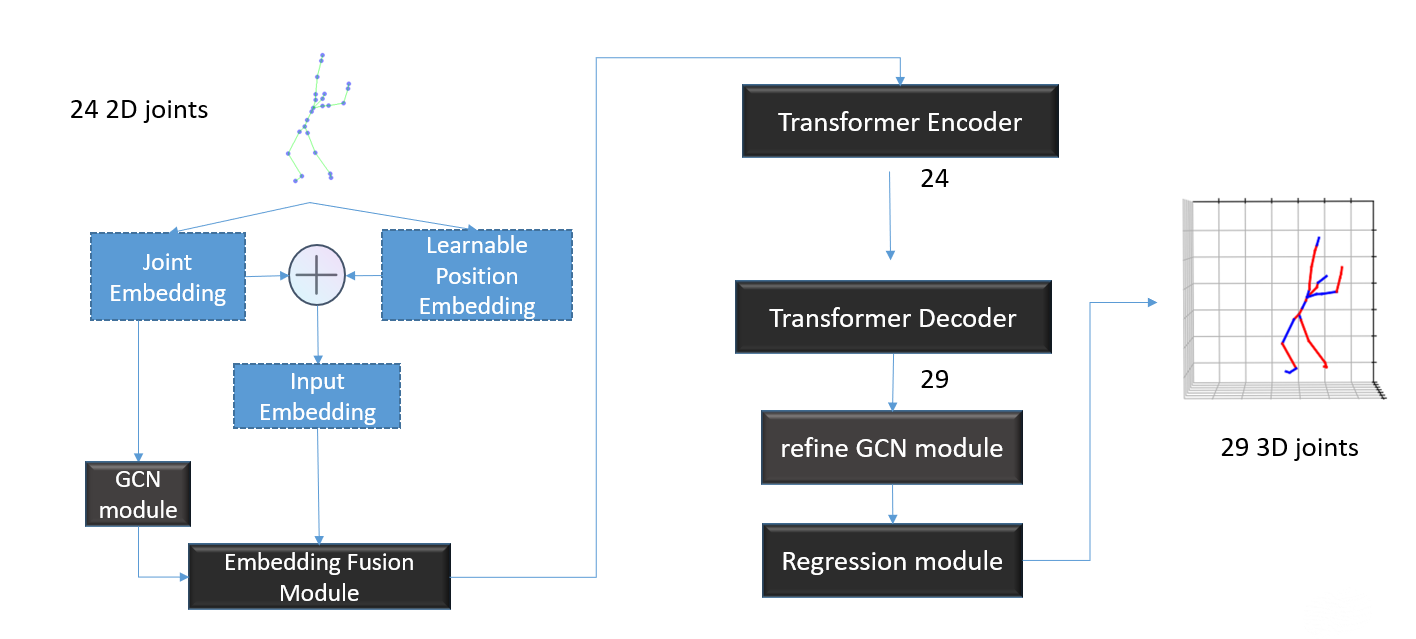
Flowchart for our jointlifter which lifts 2D joints to 3D. This shows as (b) in the system flowchart.
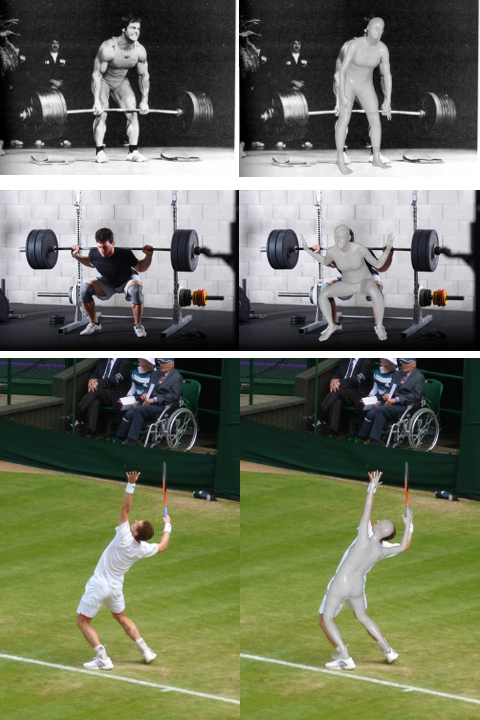
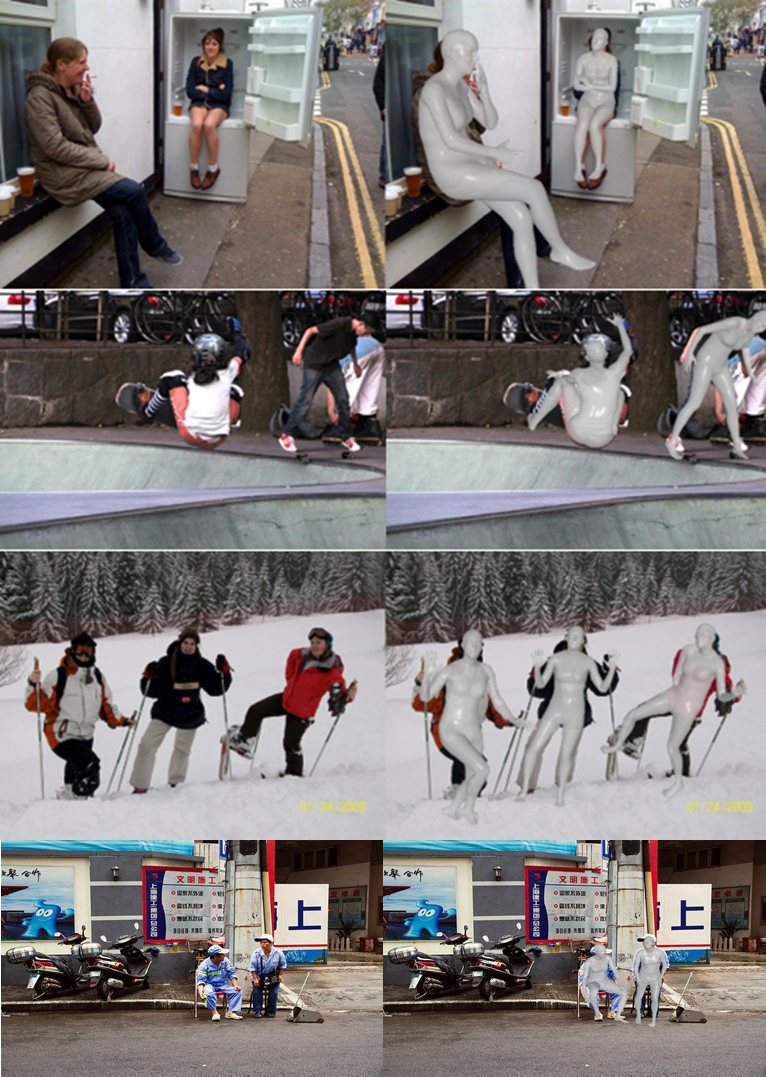


Results of generating smpl on images with one or multiple people.
[基於利用Transformer和GCN架構來解決SMPL逆向運動學的3D人體姿態估計方法]
3D human pose and shape estimation is essential for applications such as animation, virtual reality, and human-computer interaction because it can provide accurate and realistic human models. In this thesis, we present a comprehensive system that integrates techniques from multiple research fields for 3D human pose and shape estimation from a single 2D image. Our approach employs a multi-resolution Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for predicting accurate 2D human joints, a Transformer-GCN architecture method for lifting 2D joints to 3D, and an SMPL (Skinned Multi-Person Linear) model-based Inverse Kinematics (IK) solution for determining SMPL parameters. We optimize the system by fine-tuning components to utilize human body geometric constraints for better prediction accuracy. Additionally, we adapt Transformer-GCN to better recognize geometric constraints of the human body and handle sequential human joint data instead of traditional temporal inputs like video frames. This integrated technique allows for more precise and contextually aware joint estimations and achieves more accurate Inverse Kinematics solutions. Our approach outperform previous state-of-the-art shemes across various 3D human pose and shape benchmarks by 7.7mm MPJPE (Mean per joint position error) value on 3DHP dataset and 7.9mm MPJPE value on Human3.6M dataset.
SUMMARY (中文總結):
3D人體姿態與形狀估計在動畫、虛擬現實和人機互動等應用中非常重要,因為它能生成準確而逼真的人體模型。
在本論文中,我們提出了一個完整的系統,用於從單張2D圖像中估計3D人體姿態與形狀。我們的方法包括使用多分辨率卷積神經網絡(CNN)
來準確預測2D人體關節,使用Transformer-GCN架構將2D關節提升到3D,以及基於SMPL(Skinned Multi-Person Linear)模型的逆向運動學(IK)
方法來計算SMPL參數。我們通過調整系統中的各部分來提高整體性能,並利用人體幾何結構的特性來提升預測的準確性。此外,我們改進了Transformer-GCN
,讓它更好地處理人體結構約束,並支持順序性人體關節數據,而不是依賴傳統的視頻幀序列輸入。這種整合的方法讓關節估計更精準,也讓逆向運動學的計算更準確。
我們的系統在多個3D人體姿態與形狀基準數據集上的表現超越了現有技術,在3DHP數據集上平均每關節位置誤差(MPJPE)降低了7.7毫米,在Human3.6M數據集上降低了7.9毫米。
RESULTS:
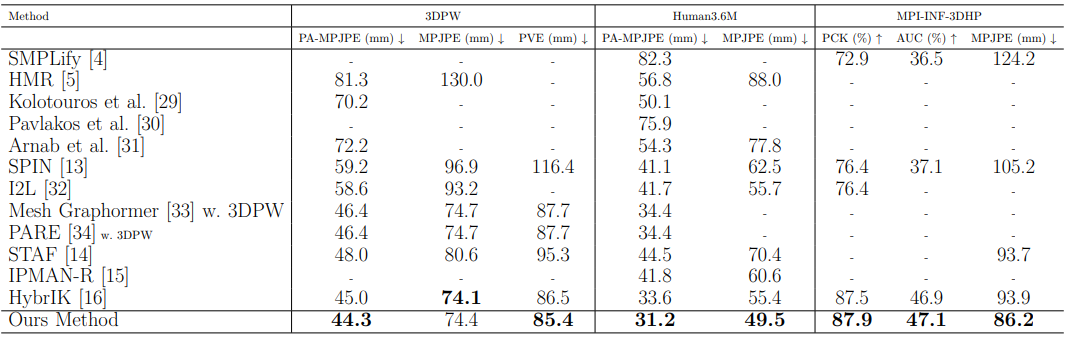
Comparison with other methods on 3D Human Pose and Shape Estimation Benchmark (3DHP, Human3.6M datasets, 3DPW).
REFERENCES:
[1] M. Loper, N. Mahmood, J. Romero, G. Pons-Moll, and M. J. Black, “SMPL: A skinned multi-person linear model,“ ACM Trans. Graphics (Proc. SIGGRAPH Asia), vol. 34, no. 6, pp. 248:1-248:16, Oct. 2015.
[2] J. Li, C. Xu, Z. Chen, S. Bian, L. Yang, and C. Lu, “Hybrik: A hybrid analytical-neural inverse kinematics solution 3d human pose and shape estimation,“ in Proceedings 838 of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3383-3393, 2021.
[3] A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A. N. Gomez, L. Kaiser, and I. Polosukhin, “Attention is all you need,“ 2023.
[4] H. Kang, Y. Wang, M. Liu, D. Wu, P. Liu, and W. Yang, “Double-chain constraints for 3d human pose estimation in images and videos,“ arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.05298, 2023.